Since Bitcoin’s grand entrance in 2009, the crypto landscape has become incredibly diverse. From Ethereum to Dogecoin, there’s no shortage of digital currencies vying for your attention. But amidst this crowded field, some have stood out and found real-world applications.
Unlike digital currencies that remain confined to niche uses or have faded away, Ripple has carved out a unique space. Over the years, they’ve gained momentum and are now integral to several financial systems, including some major banks. It’s not just about trading or investing; Ripple facilitates real-world solutions, especially in international payments.
This comprehensive guide will explore what makes Ripple a noteworthy contender in the crypto world. We’ve covered everything, from its advantages and use cases to its role in financial ecosystems.
What is Ripple?

In today’s globalized world, one would expect transferring money across borders to be straightforward. However, that’s far from the reality. Old financial systems like SWIFT are slow and costly because they use outdated technology and have multiple transaction layers.
Ripple aims to address these inefficiencies.
Created from the start to replace SWIFT, which only facilitates the messaging of payment orders between banks worldwide without actually settling and clearing transactions, Ripple is designed to send and settle transactions.
It’s a distributed ledger technology that provides an efficient, faster, and more affordable network for cross-border payments.
So, what sets Ripple apart? It acts as a trusted intermediary in transactions, ensuring that exchanges are conducted smoothly and efficiently. Ripple is versatile; it can facilitate transactions for fiat currencies, such as the U.S. dollar, and cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
One unique aspect of Ripple is its use of its own digital currency, XRP, to handle transaction fees. The fees for using Ripple are very low (just 0.00001 XRP), which is much cheaper than the high fees usually charged by traditional systems for sending money abroad.
In simple terms, Ripple is not just a digital currency or a company. It’s a way to transfer money worldwide that could change the game.
History of Ripple
While Bitcoin often takes the spotlight as a groundbreaking technology, it’s worth noting that the ideas behind Ripple predate Bitcoin by several years. The journey began around 2004-2005 when a Canadian programmer named Ryan Fugger developed RipplePay. He aimed to offer secure payment options through a global network, but it was just the tip of the iceberg.
Fast forward to 2011, and the landscape changed dramatically. Developers Arthur Britto, Jed McCaleb, and David Schwartz created the XRP Ledger, an open-source blockchain designed to tackle the inefficiencies plaguing traditional cross-border payments. Chris Larsen later joined the trio, and together, they founded the company we now know as Ripple.
Although related, Ripple and XRP are separate entities. Initially known as OpenCoin, Ripple is a fintech company that underwent a couple of rebrandings before settling on its current name in 2015. On the other hand, XRP is a digital asset running on the XRP Ledger, serving as the backbone for Ripple’s various payment products.
As of September 2023, XRP boasts a market cap of around $26 billion, making it a top 5 cryptocurrency. Despite this, Ripple and XRP maintain distinct identities, at least on paper. Ripple focuses on building global payment products, while XRP is a versatile digital asset used for various applications, from online payments to currency swaps.
How Does Ripple work

Regarding cross-border payments, traditional systems often involve multiple intermediaries, each adding time and cost to the process. Ripple’s blockchain technology aims to simplify this by providing a more direct and efficient route for transactions.
At its core, Ripple uses a consensus algorithm, different from the proof-of-work system used by Bitcoin or the proof-of-stake used by Ethereum. This consensus algorithm allows for quicker validation of transactions without the need for as much computational power. In simpler terms, it’s a more energy-efficient way to reach agreement across the network.
Ripple’s blockchain is not entirely decentralized; it operates on a network of validating servers, including those owned by banks and market makers. These servers work together to agree on the order and validity of transactions. This hybrid approach best combines centralized and decentralized systems, aiming to offer speed and security.
One of the standout features is the Ripple Protocol Consensus Algorithm (RPCA), which is applied every few seconds by all Ripple servers to maintain the accuracy and agreement of the network. Each server compiles a list of “candidate” transactions, which are then voted on to either be included or excluded from the ledger – a process that ensures integrity and mutual agreement on the network.
XRP, the digital asset used in the Ripple network, is a crucial bridge between different fiat currencies, allowing money to be transferred and settled more efficiently.
Before we move on, it’s essential to highlight some crucial components that make up the Ripple blockchain. Understanding these elements will give you a more rounded view of how Ripple aims to improve cross-border payments.
RippleNet
RippleNet is the network on which all Ripple payments are processed. It connects various parties (like banks and money service businesses) and allows for the transfer of value within the network in a secure, instant, and low-cost way. RippleNet is often considered the backbone of Ripple’s offering, connecting disparate financial systems under one umbrella.
XRP Ledger
We’ve mentioned this before, but it’s worth diving deeper. The XRP Ledger is an open-source blockchain protocol, the foundation supporting the digital asset XRP. The ledger is maintained by a network of independent validating servers owned by banks, market makers, or Ripple itself. The XRP Ledger aims to provide more transactional privacy and security than traditional payment systems.
Gateways
In the Ripple network, gateways serve as the entry points to the network. They accept currency deposits, issue corresponding IOUs, and handle withdrawals. Gateways are trusted intermediaries, usually banks, crucial for facilitating money movement in and out of the Ripple ecosystem.
As of 2023, Ripple has been focusing on expanding its On-Demand Liquidity (ODL) services, which use XRP to source liquidity and reduce costs. This is particularly beneficial for businesses that need to make frequent cross-border transactions.
The Ripple blockchain is a complex yet elegantly designed system that aims to streamline cross-border payments and financial transactions. From RippleNet’s interconnected financial institutions to the XRP Ledger’s open-source protocol and the essential role of gateways, each component plays a vital part in making Ripple a standout player in the digital asset space.
What is XRP?

You’ve heard about Ripple, but what about XRP? Mixing the two is easy, but they’re not the same. XRP is the digital currency that fuels transactions on Ripple’s RippleNet. Think of it as the gas in your car – necessary for the journey but different from the vehicle itself.
Originally, XRP got its name from xRapid, another product from Ripple used by financial institutions as a bridge currency. Unlike many cryptocurrencies mined over time, all 100 billion XRP tokens were created upfront – in fact, you can’t mine Ripple’s XRP.
Because all XRP tokens were pre-mined, the supply is fixed. That means no more XRP will ever be created. This fixed supply eliminates the need for proof of work, the energy-consuming process of mining other cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
Ripple holds about 45 billion in an escrow account, while the rest circulates among users globally.
Like Satoshi for Bitcoin, the XRP coin has a subunit called a “drop,” which is one-millionth of an XRP. It’s like cents to a dollar but way smaller.
What sets the XRP coin apart? Ripple (XRP) is designed to make international payments more efficient and less costly. It acts as a bridge between crypto and fiat currencies, making trading easier for financial institutions.
But keep in mind, that using XRP isn’t without risks, especially given the volatility of crypto.
One of XRP’s standout features is its low transaction fees – just 0.00001 XRP (10 drops) for a standard trade. Plus, it’s scalable, handling up to 1,500 transactions per second. And if you’re eco-conscious, you’ll be happy to know that XRP is carbon-neutral and energy-efficient.
Further Reading: Ripple Increases XRP Ledger Transactions Per Second from 1,500 to 3,400
Roles of XRP in the Ripple Ecosystem
Understanding XRP involves more than just knowing it’s a cryptocurrency. It is crucial in Ripple’s ecosystem, particularly within the XRP Ledger (XRPL). This ledger is a secure digital record that tracks all transactions, from account balances to transfers. Security is ensured through cryptographic key pairs, and only private key holders can authorize transactions.
XRP transactions are lightning-fast, settling in mere seconds. This transaction speed is great for financial institutions that must bridge different currencies. A network of over 150 validators oversees the XRPL. The best among them are included in Ripple’s Unique Node List, which confirms the legitimacy of transactions.
The system is designed to handle flawed validators as well. If flawed validators exceed 20% of the total, the network stops functioning, ensuring integrity.
XRP serves multiple purposes. It’s particularly useful for less commonly traded currencies, which often require an intermediary like the U.S. dollar. With XRP, the cost of these transactions is significantly reduced.
XRP isn’t just about transactions. It’s also the backbone of the XRPL’s decentralized exchange (DEX), which has been up and running since 2012. This DEX allows for trading between XRP and other cryptocurrencies at minimal fees. Plus, it recently got a boost with Allbridge integrating support for XRPL, opening doors for Ripple in the DeFi space.
Important Advantages of Ripple for Businesses
As businesses explore the potential of blockchain technology, Ripple advantages stand out for several compelling reasons. Here’s why it’s becoming a go-to choice for many organizations:
Reliability and Trust
RippleNet, the platform on which XRP operates, is backed by a global network of 150 validators. This robust infrastructure has garnered trust among major financial institutions worldwide, making it a reliable choice for secure transactions.
Cost-Effectiveness
Ripple’s use of “drops” as the smallest transaction unit makes it incredibly cost-effective. This low-cost structure is particularly appealing for businesses looking to maximize efficiency without compromising on security.
Scalability
Unlike traditional blockchain systems that can be limited in their transaction processing capabilities, Ripple can handle a large volume of transactions per second. This makes it ideal for fintech companies needing a robust and scalable crypto payment gateway.
Speed is of the Essence
One of the major drawbacks of using Bitcoin for transactions is its slow processing time. Ripple addresses this issue head-on by offering transaction confirmations in just 3-5 seconds, a significant improvement over Bitcoin’s average of 20 minutes.
Sustainability
In today’s world, sustainability isn’t just a buzzword; it’s a necessity. Ripple is ahead of the curve in this aspect. Unlike other cryptocurrencies that require energy-intensive mining processes, Ripple’s network operates efficiently with minimal energy consumption. This aligns well with the sustainability goals of many companies and even meets certain regional compliance requirements.
These Ripple benefits make the technology attractive for businesses leveraging blockchain technology.
Some Ripple Use Cases
Regarding practical applications, Ripple is more than just a theoretical marvel. From providing on-demand liquidity to streamlining cross-border payments, here are some real-world use cases that showcase the benefits of Ripple.
On-the-Spot Liquidity: A Game-Changer for Banks
In traditional banking systems, the receiving bank gets paid before the settlement, which can take 2-3 days. Ripple’s XRP offers a solution to this delay by providing “On-Demand Liquidity.” This feature speeds up real-time settlements and reduces the need for intermediaries, making it a compelling option for institutional investors.
Making Cross-Border Payments Seamless
One of the standout benefits of Ripple is its ability to simplify cross-border payments. By using XRP as a bridge currency, Ripple enables real-time settlements between parties with different native currencies. This eliminates the need for middlemen and minimizes the risk of currency fluctuations, making Ripple cross-border payments both efficient and cost-effective.
The Role of Gateways in Ripple Transactions
Ripple employs a mechanism known as a gateway to establish trust between transaction parties. Acting as a credit intermediary, the gateway facilitates the transfer of various currencies to public addresses within the Ripple network. This adds another layer of security and efficiency to the transaction process.
Major Banks Using XRP: Partnerships That Speak Volumes
Several major banks and other financial institutions have partnered with Ripple, integrating XRP into their payment systems.
For instance, Bank of America has been in a long-standing partnership with Ripple, which is crucial in establishing compliance standards for international payments on RippleNet.
Similarly, Standard Chartered Bank joined forces with Ripple to extend its payment services to over 50 countries, thereby increasing its global footprint.
Santander Bank and Thailand’s Siam Commercial Bank are other notable examples of financial institutions that have reaped the benefits of Ripple technology.
Ripple Benefits vs. Bitcoin
When it comes to cryptocurrencies, Bitcoin is often the first name that comes to mind. However, Ripple’s XRP has been making waves in the financial world, offering features that set it apart from its more famous counterpart.
In this section, we’ll put XRP vs. Bitcoin head-to-head, examining key aspects like ownership, processing speed, and more. Let’s dive into the details with a comparative table.
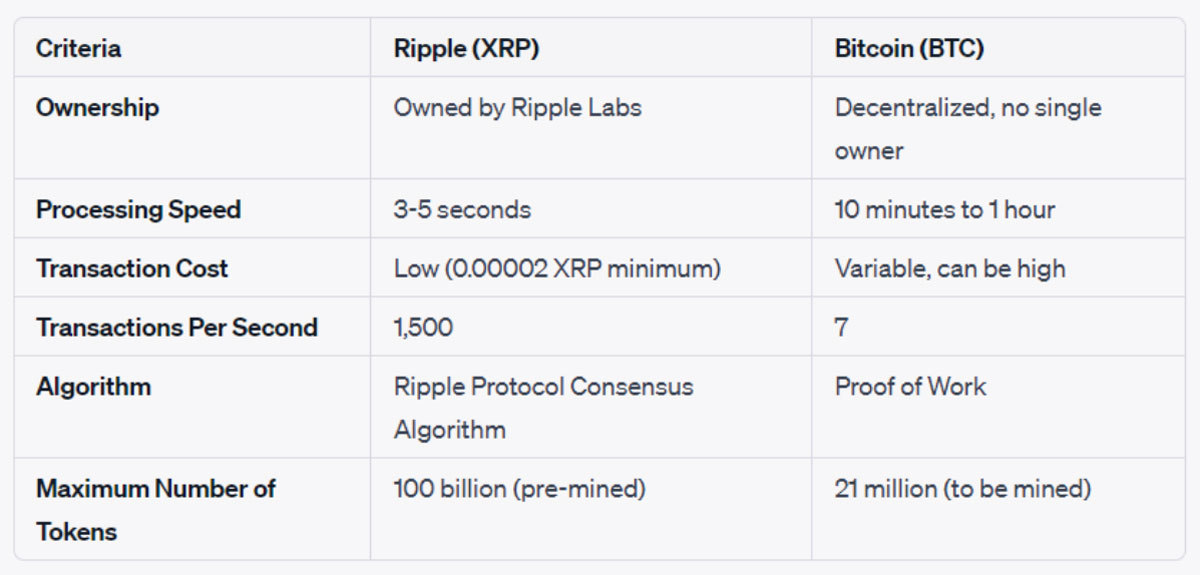
As you can see, Ripple and Bitcoin have distinct advantages and limitations. While Ripple excels in processing speed and transaction cost, Bitcoin stands out for its decentralized ownership and robust security algorithm.
The Future of Ripple: A Financial Game-Changer
Ripple is more than just a cryptocurrency; it’s a technology poised to significantly impact the global financial industry. From potentially replacing the dated SWIFT network to offering fast and cost-effective transactions, Ripple is setting the stage for a financial revolution.
One of Ripple’s key initiatives is the Liquidity Hub, launched in 2019 for enterprise clients. This hub serves as a one-stop shop for accessing digital assets from various providers, including exchanges and OTC desks.
It offers an enterprise-level dashboard for seamless digital asset management, trading, and reporting, bridging the gap between traditional fiat currencies and the burgeoning world of digital assets.
As the crypto world expands into DeFi and NFTs, Ripple is keeping pace with projects in these areas, including a $250 million creator fund for NFTs creators to mint their projects onto XRP Ledger.
It’s also positioning itself as a leader in Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), offering a robust platform for their management.
In a significant development that underscores its potential, Ripple recently secured a landmark win in its case with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). This victory clears a major legal hurdle and could be pivotal for Ripple’s widespread adoption and success.
Ripple is more than a cryptocurrency; it’s a technology set to reshape the financial landscape.
Ready to Ride the Ripple Wave? Start Accepting XRP with CoinPayments Today!
So, now that you know what is Ripple and you’re probably wondering, “What’s next?”
Well, if you’re as excited as we are about the future of global payments, why not be a part of it?
With CoinPayments, accepting XRP is as easy as pie.
You’ll not only be riding the wave of financial innovation but also offering more flexible payment options to your customers. Ready to get started? Set up your CoinPayments account and begin accepting XRP today.




